Water
Water Potential
Water potential (ψ) is the measure of potential energy in water and drives the movement of water through plants.
Osmosis
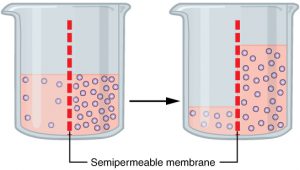
If two solutions of different concentration are separated by a semi-permeable membrane – which is permeable to the smaller molecules but not the larger ones – the solvent will tend to diffuse across the membrane from the more concentrated solution to the less concentrated.
Image yy OpenStax – https://cnx.org/contents/FPtK1zmh@8.25:fEI3C8Ot@10/Preface, CC BY 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30131189
Diffusion
Diffusion refers to the process in which molecules intermingle as a result of their kinetic energy of random motion.
Facilitated Diffusion (Facilitated transport)
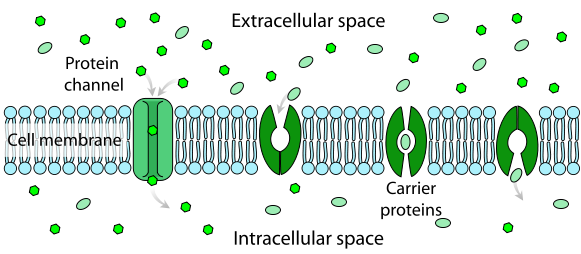
Facilitated Diffusion is a form of passive transport across a biological membrane in which transport protein facilitates (or mediates, or catalyzes) the movement of an otherwise membrane-impermeant molecule, or ion, across the plasma membrane down its concentration, or electrochemical gradient.
Active Transport
A solute can move from lower concentrations up to higher concentrations. This process works similar to facilitated diffusion but requires energy to be achieved.





You must be logged in to post a comment.